iShredder™ Android® Business
Secure data erasure for businesses
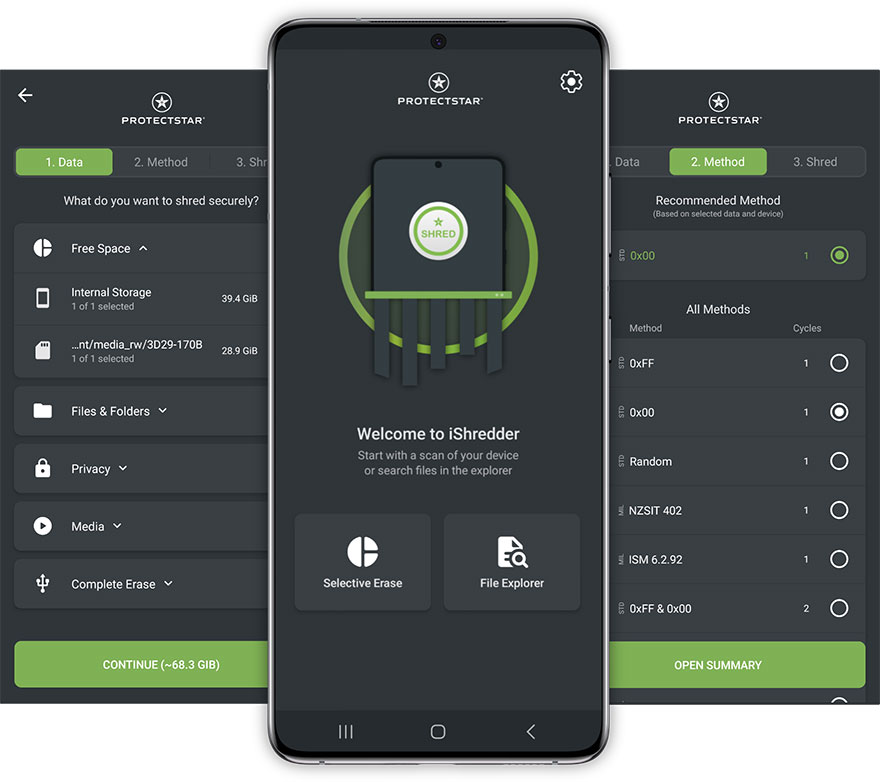

What is iShredder™?
iShredder™ is the most popular data shredder for iOS, Android, Windows, Mac, and Windows Server. Since 2010, the secure erasure software has been used by over 8,000,000 users in over 100 countries worldwide.
iShredder™ erases so securely with international military security standards that defense departments and government agencies even use the technology.
Erase data irrevocably on Android.
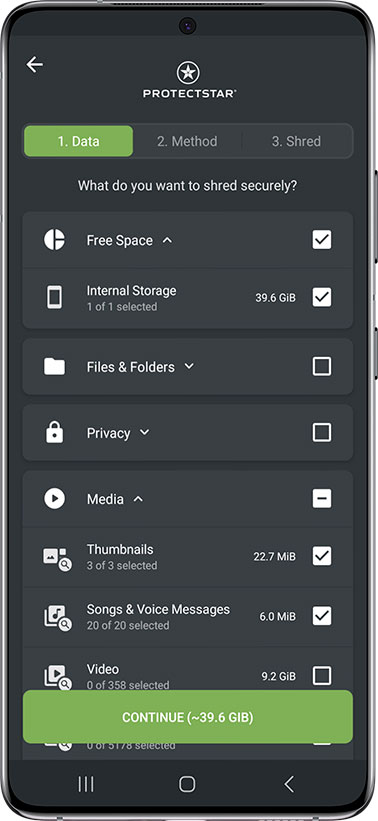
Suppose files, photos, SMS/MMS, call logs, and contacts have been manually deleted. In that case, this deleted data can be recovered from the Android device's free space until the data has been overwritten using secure deletion algorithms.
In just three steps, data is erased according to patented security standards, and recovery becomes impossible:
![Select the data]()
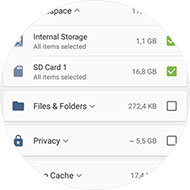
1. Select the data
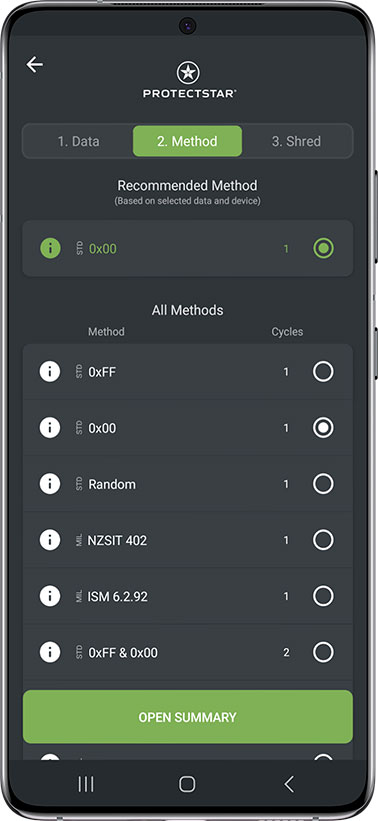
![Choose the method]()
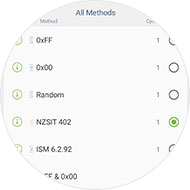
2. Choose the method
![Begin to erase]()
3. Begin to erase
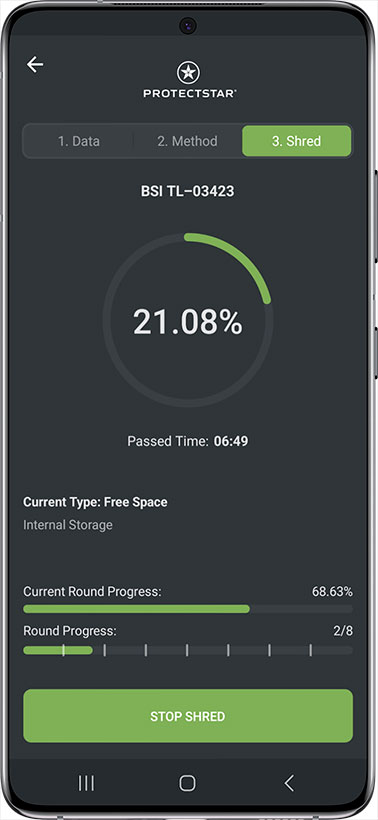
Secure Android® Device Erasure?
Today, with little effort, it's easy to recover allegedly deleted data such as notes, passwords, address books, WhatsApp, videos, calendars, and much more from your Android® device's memory.
If you or your company want to sell or pass on an Android® smartphone or tablet, the data stored on it must be securely deleted and not recoverable by third parties. You will need a deletion log as proof.
What data is still in the free memory?
When you delete a file, such as a photo, the operating system only removes the association to this file but does not delete it from memory. Instead, the corresponding sector is marked as "free" by the Android operating system, so another file can use this memory block again.
With the award-winning "Securely Erase Free Memory" feature in iShredder™Android Government Edition, free memory can be securely overwritten so that previously deleted data cannot be recovered.
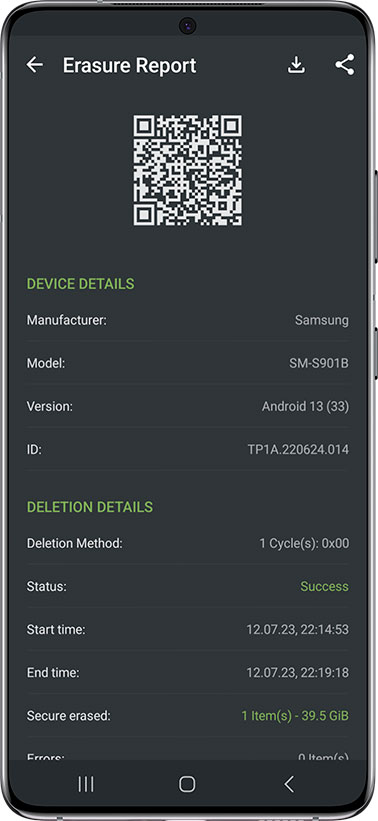
Erasure Reports
Data erasure is overwriting the data in every sector. This will make recovering the data impossible.
After erasing your data, iShredder™ will generate a report which you could use for the audit trail, the proof of erasure. It provides auditable and verifiable assurance that all data was sanitized in compliance with published standards such as GDPR, UK Government InfoSec No. 5, U.S. DoD, NIST 800-88.

Exceeds international standards
With over 20 recognized erasure algorithms, iShredder™ exceeds international government and military security standards for secure data erasure. Each deletion method has been analyzed for security by government agencies or independent organizations and ensures the destruction of data.
Erasure algorithms such as DoD 5220.22-M E, US Air Force (AFSSI-5020), BSI-2011-VS, US Army AR380-19, DoD 5220.22-M ECE, BSI/VS-ITR TL-03423, CSEC ITSG-06, NATO Standard, Gutmann, HMG InfoSec No.5, DoD 5220.22 SSD and others are available in the iShredder™.

DSGVO-compliant data erasure
With the European Data Protection Regulation (EU-DSGVO), new requirements for secure data erasure have come to all companies.
If sensitive information falls into the wrong hands, lost business, fines, or reputational damage can result. In addition to the DSGVO Art.17 "Right to Erasure" https://gdpr-info.eu/art-17-gdpr//, data protection laws require fully documented data destruction.
iShredder™ offers all DSGVO-compliant data erasure incl. detailed erasure reports.
More than TWENTY
methods of erasure








In a sector where trust and security are primary concerns, Protectstar™ provides his customers with only modern and first-class products: iShredder™ offers more than twenty secure deletion methods that certified by government and military organizations.
Erasure Algorithm:
- 50 Cycles: Protectstar SDA (2007)
- 35 Cycles: Gutmann method
- 8 Cycles: German BSI TL-03423
- 7 Cycles: NATO Standard
- 7 Cycles: DoD 5220.22-M ECE
- 7 Cycles: CANADIAN RCMP TSSIT OPS-II
- 5 Cycles: BSI-2011-VS
- 4 Cycles: Protectstar ASDA (2017)
- 4 Cycles: DoD 5220.22-M E for SSD
- 3 Cycles: Canadian CSEC ITSG-06
- 3 Cycles: HMG Nr. 5 extended
- 3 Cycles: AFSSI-5020
- 3 Cycles: NAVO P-5239-26 (MFM)
- 3 Cycles: NAVO P-5239-26 (RLL)
- 3 Cycles: US Army AR380-19
- 3 Cycles: DoD 5220.22-M E
- 3 Cycles: NCSC-TG-025
- 3 Cycles: NIST SP 800-88
- 2 Cycles: RUSSIAN GOST R 50739-95
- 1 Cycle: Australian ISM 6.2.92
- 1 Cycle: 0XFF for SSD
- 1 Cycle: Random Values
- 1 Cycle: NIST SP 800-88 Rev. 1 (2014)

Specifically developed by Protectstar™ Inc. in 2007 it runs through fifty erasure routines.
Data will be overwritten for two times with a random value, afterwards with their complements. It includes and the DoD 5220.22-M (E) standard and Peter Gutmann method and random algorithms.
The algorithm from Peter Gutmann was found in 1996 and makes 35 overwrite passes in total.
This algorithm is one of the state-of-the-art methods for data destruction.
In March 2010 the German Federal office for IT Security (BSI) published a new technical BSI Guideline for "Requirements to overwrite memory media".
The method is similar to VSITR standard for magnetic storage media.
In total the new algorithm has 8 cycles, which has to be worked through in chronological order. Includes one cycle of verification.
The NATO method is the deletion standard of North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO).
It will overwrite the target data area 7 times.
The first six overwrites are with the fixed values (0x00) and (0xff), alternating between passes.
The 7th overwrite is with a random value i.e. 0x00,0xFF,0x00,0xFF,0x00,0xFF and 7th pass with a random value.
The method for high security is based on the January 1995 'National Industrial Security Program Operating Manual'by the Department of Defense (DoD).
In this seven cycle variation (DoD 5220.22-M ECE), data is first overwritten three times with DoD 5220.22-M (E) Standards, then with a specific random value, and finally once again with DoD 5220.22-M (E).
The Royal Canadian Mounted Police Standard RCMP TSSIT OPS-II overwrites data securely with alternating sequences with a total of seven cycles.
The German Federal office for IT Security (BSI) describes in the technical BSI guideline for 'Requirements to overwrite memory media' from July 2010 the modern method BSI-2011.
This clause includes 5 steps, which is implemented in sequential order.
This method is specially developed for SSD (Solid State Drive) and flash memory, based on the U.S.
Department of Defense's standard DoD 5220.22-M E. It will overwrite data four times.
This method is specially developed for SSD (Solid State Drive) and flash memory, based on the U.S.
Department of Defense's standard DoD 5220.22-M E. It will overwrite data four times.
The Canadian CSEC ITSG-06 sanitization method has three cycles and was published in 2006 by Communication Security Establishment Canada (CSEC).
The HMG Infosec Standard No 5 - enhanced level is approved to wipe UK Government Top Secret data and has also been approved by NATO.
The algorithm is a three pass overwriting algorithm: first pass - with zeros (0), second and third passes with its compliment and random values(with last pass verification).
The AFSSI-5020 sanitization method was originally defined in the Air Force System Security Instruction 5020 by the United States Air Force (USAF) in 1996 and may still be today.
This is the US Navy standard NAVSO P-5239-26 for MFM encoded drives.
This deletion method first writes the fixed value (0xffffffff) to the target data area, then the fixed value (0xbfffffff) and then random values.
Finally, the target data area is read to verify the overwrites.
This is the US Navy standard NAVSO P-5239-26 for RLL encoded drives.
This deletion method first writes the fixed value (0xffffffff) to the target data area, then the fixed value (0x27ffffff) and then random values.
Finally, the target data area is read to verify the overwrites.
AR380-19 is the data shredding algorithm specified and published by the U.S. Army.
The algorithm is a three pass overwriting algorithm: first pass - with random bytes, second and third passes with certain bytes and with its compliment (with last pass verification).
The method for low security but for high execution speed is based on the January 1995 'National Industry Security Program Operating Manual' from the DoD (US DoD 5220.22-M).
The variation (DoD 5220.22-M E) offers 3 cycles in which the data are overwritten with first a set value, then its compliment, and then a random value.
The American NCSC-TG-025 standard of the National Computer Security Center (NCSC) securely overwrites existing information on a data medium three times.
The in 2006 released standard is the Special Publication 800-88 from NIST, which is the go-to data erasure standard for organizations in the United States. Its principles can apply to magnetic, flash-based, and other storage technologies, from USB drives to servers.
The Russian data deletion standard GOST R 50739-95 for secure data erasure overwrites the target data are two tome. In the first pass with a zero, and in the second pass with random characters.
ISM 6.2.92 is the Australian government's data sanitization standard.
The method was originally defined in the Information Security Manual (ISM) issued by the Australian Department of Defense: Intelligence & Security.
The ISM 6.2.92 sanitization can not be used to sanitize classified information.
This method is specially developed for SSD (Solid State Drive) and flash memory.
It offers one cycle which data are overwritten by the pattern "0xFF".
This method for lowest security but for very high execution on speed. It offers only one cycle which data are overwritten with random values.
In December 2014, the guidelines were revised, making the current version “NIST Special Publication 800-88 Rev. 1”.
See here the description of the method you have selected.
iShredder™ Android Business
- Securely erase any kind of data
- Securely overwrite the freespace
- Secure freespace wipe of SD card
- Preinstalled standard deletion algorithms
- Wipe methods in total: 25
- Secure delete external usb sticks, hard disk, etc.
- Securely Erase files and folders
- Securely Erase media files
- Securely Erase contacs and clipboard
- Securely Erase SMS, MMS and call logs
- Additional Enterprise and Government erasure methods
- Create and Export Erasure Reports
- Password Protection
- Volume license model for Enterprise customers
- Including 12-months technical support and updates/upgrades